Here are the Commands start from :
1. cleanmgr
2. %userprofile%
3. control
4. %programfiles%
5. compmgmt.msc
6. firewall.cpl
7. fsmgmt.msc
8. Open Web Browser (iexplore, chrome, firefox, opera)
9. msinfo32
10. Netplwiz




The ability to perform tasks from a system’s command line allows those tasks to be used in batch files. This recipe describes several uses of taskkill to terminate Windows processes.
If you know the name of a process to kill, for example notepad.exe, use the following command from a command prompt to end it:
taskkill /IM notepad.exe
This will cause the program to terminate gracefully, asking for confirmation if there are unsaved changes. To forcefully kill the same process, add the /F option to the command line. Be careful with the /F option as it will terminate all matching processes without confirmation.To kill a single instance of a process, specify its process id (PID). For example, if the desired process has a PID of 827, use the following command to kill it:
taskkill /PID 827
Using filters, a variety of different patterns can be used to specify the processes to kill. For example, the following filter syntax will forcefully kill all processes owned by the user Quinn:
taskkill /F /FI “USERNAME eq Quinn”
The following table shows the available filters and their use.
Filter Name Valid Operators Valid Value(s)
———– ————— ————–
STATUS eq ne RUNNING | NOT RESPONDING
IMAGENAME eq ne Image name
PID eq ne gt lt ge le PID value
SESSION eq ne gt lt ge le Session number.
CPUTIME eq ne gt lt ge le CPU time in the format
of hh:mm:ss.
MEMUSAGE eq ne gt lt ge le Memory usage in KB
USERNAME eq ne User name in [domain\]user
format
MODULES eq ne DLL name
SERVICES eq ne Service name
WINDOWTITLE eq ne Window titleeq: equals ne: not equal
gt: greater than lt: less than
gt: greater than or equal le: less than or equal
As my project work requires writing and running codes, I generally have at least one Windows command prompt open. If this is the case with you then it is much faster to manage your windows processes from command prompt than to open up the Task Manager, just like we do on Linux using “ps” and “kill” command. Get to know the following commands and you can easily use the command prompt to see and kill processes.
1. Tasklist : This command is similar to “ps” command on Linux and is used to see the details of the programs and processes that are running in Windows. Tasklist can be applied to see how much memory and CPU time running processes are using, what DLL files they rely on, and other information. Thus it can be a very useful troubleshooting tool.
tasklist on the command prompt, you can see the following informations by default. Image Name, PID, Session Name, Session#, Mem Usagetasklist /vtasklist /svc to get a table relating Image Name, PID, and Services, very useful to know the relationship between a process and the services that are running on a system.tasklist /m to find which DLLs are used by each process.tasklist /fi "status eq not responding"tasklist /fi "memusage gt 10000"tasklist /? or refer to Microsoft’s documentation.(NOTE: Although Tasklist is a part of Windows XP Professional, it does not come with the Home edition. Those with the Home version of XP can download this file and can put it in the system path.)
2. Tskill : This command is used to end a process, using its name of its PID.
tskill processname to kill a process with name processname. For example: tskill winword (closes all the Microsoft documents that you have open)tskill processid to kill a process with PID processid. Tasklist can be used to find the PID of a process.tskill /? or refer to Microsoft’s documentation.(NOTE: Tskill is a part of both Windows XP Professional and the Home edition.)
3. Taskkill : Similar to Tskill, this command is also used to end a process but it provides us more options in doing so. Apart from specifying the PID or the image name of the process to kill, we can also use ceratin filters to kill the matching processes as explained below.
taskill /IM imagename to kill a process with the given Image name. For example:taskkill /im notepad.exe /f (forces notepad to be killed.)taskill /PID processid to kill a process with the given processid.taskkill /f /fi "status eq not responding"taskkill /f /fi "memusage gt 10000"taskkill /? or refer to Microsoft’s documentation.(NOTE: Taskkill is only a part of Windows XP Professional.)
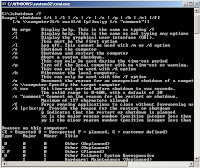


nslookup [-option] [hostname] [server]
C:\> nslookup
Default Server: nameserver1.domain.com
Address: 10.0.0.1
>
Commands: (identifiers are shown in uppercase, [] means optional)
NAME - print info about the host/domain NAME using default
server
NAME1 NAME2 - as above, but use NAME2 as server
help or ? - print info on common commands
set OPTION - set an option
all - print options, current server and host
[no]debug - print debugging information
[no]d2 - print exhaustive debugging information
[no]defname - append domain name to each query
[no]recurse - ask for recursive answer to query
[no]search - use domain search list
[no]vc - always use a virtual circuit
domain=NAME - set default domain name to NAME
srchlist=N1[/N2/.../N6] - set domain to N1 and search list to N1, N2,
and so on
root=NAME - set root server to NAME
retry=X - set number of retries to X
timeout=X - set initial time-out interval to X seconds
type=X - set query type (for example, A, ANY, CNAME, MX,
NS, PTR, SOA, SRV)
querytype=X - same as type
class=X - set query class (for example, IN (Internet), ANY)
[no]msxfr - use MS fast zone transfer
ixfrver=X - current version to use in IXFR transfer request
server NAME - set default server to NAME, using current default server
lserver NAME - set default server to NAME, using initial server
finger [USER] - finger the optional NAME at the current default host
root - set current default server to the root
ls [opt] DOMAIN [> FILE] - list addresses in DOMAIN (optional: output to
FILE)
-a - list canonical names and aliases
-d - list all records
-t TYPE - list records of the given type (for example, A, CNAME,
MX, NS, PTR, and so on)
view FILE - sort an 'ls' output file and view it with pg
exit - exit the program
C:\> nslookup
Default Server: ns1.domain.com
Address: 10.0.0.1
> set q=mx
> mailhost
Server: ns1.domain.com
Address: 10.0.0.1
mailhost.domain.com MX preference = 0, mail exchanger =
mailhost.domain.com
mailhost.domain.com internet address = 10.0.0.5
>
C:\> nslookup
Default Server: nameserver1.domain.com
Address: 10.0.0.1
> server 10.0.0.2
Default Server: nameserver2.domain.com
Address: 10.0.0.2
>
ls [- a | d | t type] domain [> filename]
>ls domain.com
[nameserver1.domain.com]
nameserver1.domain.com. NS server = ns1.domain.com
nameserver2.domain.com NS server = ns2.domain.com
nameserver1 A 10.0.0.1
nameserver2 A 10.0.0.2
>
 Back to the top
Back to the topSyntax:
nslookup
nslookup host-to-find
nslookup server
interactive mode:
nslookup -server
nslookup [-options] [host-to-find ]
Options:
host [server ]
Look up information for host using the current default server or using server,
if specified. If host is an Internet address and the query type is A or PTR ,
the name of the host is returned. If host is a name and does not have a trailing
period, the default domain name is appended to the name. (This behavior depends
on the state of the set options domain , srchlist , defname , and search.
To look up a host not in the current domain, append a period to the name.
server domain
lserver domain
Change the default server to domain ; lserver uses the initial server to look up
information about domain while server uses the current default server.
If an authoritative answer can't be found, the names of servers that might have
the answer are returned.
root
Change the default server to the server for the root of the domain name space.
Currently, the host ns.internic.net is used. (This command is a synonym for
`lserver ns.internic.net' The name of the root server can be changed with
the `set root ' command.
finger [name ] [> filename ]
finger [name ] [>> filename ]
Connects with the finger server on the current host. The current host is
defined when a previous lookup for a host was successful and returned address
information (see the `set querytype=A ' command). The name is optional. > and
>> can be used to redirect output in the usual manner.
ls [option ] domain [> filename ]
ls [option ] domain [>> filename ]
List the information available for domain , optionally creating or appending
to filename The default output contains host names and their Internet addresses.
Option can be one of the following:
-t querytype list all records of the specified type (see querytype below).
-a list aliases of hosts in the domain; synonym for `-t CNAME '
-d list all records for the domain; synonym for `-t ANY'
-h list CPU and operating system information for the domain; synonym for `-t HINFO'
-s list well-known services of hosts in the domain; synonym for `-t WKS'
When output is directed to a file, hash marks are printed for every 50 records
received from the server.
view filename
Sort and lists the output of previous ls command(s) with more(1).
set keyword [= value ]
This command is used to change state information that affects the lookups.
run man nslookup for a full list of valid keywords.
set all Print the current value of the frequently-used options
to set Information about the current default server and host is also printed.
help
? Print a brief summary of commands.
exit Exit the program.
Nslookup has two modes: interactive and non-interactive.
Interactive mode allows the user to query name servers for information about various hosts and domains or to print a list of hosts in a domain.
Non-interactive mode is used to print just the name and requested information for a host or domain.
The options listed under the `set ' command can be specified in the .nslookuprc file in the user's home directory (listed one per line). Options can also be specified on the command line if they precede the arguments and are prefixed with a hyphen.
On this page you'll find a shorthand list of common tasks in batch files, and the command(s) that can be used to perform those tasks.
| Notes: | Many, if not most, of the commands listed here require Windows 2000 and later, some require Windows XP or later, some require Active Directory. Read more detailed information by following the links provided. |
| Depending on the Windows version, some commands (e.g. SETX and NETSVC) may require installation of a Resource Kit. |
| Task | Available command(s) or variable(s) |
|---|---|
| Add/remove computer to/from domain | NETDOM (1) |
| Counters | FOR /L or SET /A counter += 1 |
| Delays | PING |
| Current date | DATE /T or %Date% or DEBUG |
| Current directory | CD or %CD% |
| Current drive | %CD:~0,2% |
| Current time | TIME /T or %Time% or DEBUG |
| Directory of current batch file | %~dp0 |
| Drive of current batch file | %~d0 |
| Environment, permanent changes | SETX (2) |
| Firewall configuration | NETSH |
| Harddisk & volume management | DISKPART, FDISK, FORMAT, CONVERT, MOUNTVOL, VOL, CHKDSK, CHKNTFS, DEFRAG |
| Hardware inventory | WMIC |
| IP address (local) | PING %ComputerName%, NSLOOKUP %ComputerName% or IPCONFIG /ALL |
| IP address (remote) | PING, NSLOOKUP or WMIC |
| IP address (WAN) to file | WGET -O output_filename -q http://www.whatismyip.com/automation/n09230945.asp (3) |
| IP address (WAN) to screen | WGET -q -O- http://www.whatismyip.com/automation/n09230945.asp (3) |
| Logoff | Multiple commands available |
| Open a file, folder or web page | START |
| Permissions | CACLS, XCACLS (2), MMC & SECEDIT, SUBINACL (3) or SETACL (3) |
| Popup dialogs | NET Send %ComputerName% |
| Print text | NOTEPAD /P |
| Print anything | ASSOC, FTYPE & REGEDIT or REG |
| Printer management | RUNDLL32 PRINTUI.DLL,PrintUIEntry |
| Process management | Multiple commands available |
| Prompt for user input | SET /P & more |
| Read text files | FOR /F or occasionaly <> |
| Reboot | Multiple commands available |
| Registry | REGEDIT or REG |
| Service management | NET Stop, NET Start, SC or NETSVC (2) |
| Shutdown | Multiple commands available |
| Unicode to ASCII conversion | TYPE |
| User/group management | NET, DSADD, DSGET, DSMOD, DSMOVE, DSQUERY & DSRM (1) or CSVDE & LDIFDE (1) |
| Write text files | Redirected ECHO |
| Notes: | (1) | Requires Windows XP with Windows Server 2003 Administration Tools Pack, or Windows Server 2003 or later. |
| (2) | Resource Kit tool | |
| (3) | Third party tool |

NSLOOKUP has a fairly rich syntax and can be a bit confusing for those who have not worked with DNS a great deal. Therefore, I want to start out by showing you some of the basics. Although NSLOOKUP exists in both UNIX and Windows, there are some differences in the way that it behaves in the two operating systems. For the purposes of this article, I will be using the Windows version.
The first thing that you need to understand about NSLOOKUP is that when you use the NSLOOKUP command, it assumes that you are querying a local domain on your private network. You can query an external domain, but NSLOOKUP will try to search for the domain internally first. For example, the brienposey.com domain is external to my network. If I perform an NSLOOKUP against brienposey.com, NSLOOKUP returns the information that’s shown in Figure A.
Figure A: This is what happens when NSLOOKUP queries an external domain
If you look at the figure, you will see that there are non existent domain error messages for the IP addresses 147.100.100.34 and 147.100.100.5. These are the addresses of my internal DNS servers. Below this information however is the non authoritative answer. This means that my DNS server queried an external DNS server in an effort to resolve the IP address associated with the brienposey.com domain.
Now, let’s take a look at what happens when you query an internal domain. One of the local domains on my private network is production.com. If I perform an NSLOOKUP against production.com, I get the results shown in Figure B.
Figure B: This is what it looks like when I query an internal domain
If you look at the top portion of this screen, you will notice that I’m getting the exact same non-existent domain error messages as I got when I queried an external domain. At first, this may seem puzzling. The reason why I got this error message was because I performed an NSLOOKUP outside of the NSLOOKUP shell. I will talk more about the NSLOOKUP shell in the next section. For now though, you need to know that you can enter the NSLOOKUP command by itself. When you do, you will see the familiar non-existent domain error messages, but you will then be taken to the NSLOOKUP prompt (the > sign). From there you can enter various NSLOOKUP commands. When you are done, you can use the EXIT command to return to the command prompt.
The other thing that you should notice about Figure B is the bottom portion of the output. Beneath the reference to production.com is a string of IP addresses. These are the IP addresses of all of the domain controllers within the domain. I should also point out that if multiple IP addresses are assigned to a single server then all of the server’s IP addresses will be displayed by NSLOOKUP.
Now that I have shown you how to use the NSLOOKUP command to see the IP address or addresses associated with the domain, let’s do something a little bit more useful. One of the things that you can do with NSLOOKUP is to look up a specific type of DNS record. A good example of this is an MX record.
In case you aren’t yet familiar with all of the intricacies of DNS, the MX record points to the organization’s mail server. For example, suppose that someone wanted to send an E-mail message to you, one of the first things that their mail server would have to do is to resolve your domain’s IP address. However, a normal address resolution won’t usually work for this purpose. In Figure A, you saw that when I ran a DNS query against the brienposey.com domain, the domain resolved to the address 24.235.10.4. Keep in mind though, that this is the IP address of the server that hosts my Web site, not the address of my mail server. If someone wanted to send me an E-mail message their E-mail client would have to resolve the IP address of my domain’s mail server. This is where the MX record comes into play. The MX record is a record on a domain’s DNS server that specifies the IP address of the domain’s mail server.
As you can see, the MX record is rather important. Suppose however that your domain was having trouble receiving E-mail and you suspected that a DNS server issue was to blame. You could use NSLOOKUP to confirm that the domain does indeed have an MX record and that the MX record is pointed to the correct IP address.
Earlier I briefly mentioned that you could work within the NSLOOKUP shell. To troubleshoot an MX record problem, you pretty much have to work within this shell. Therefore, you would start the process by entering the NSLOOKUP command at the command prompt.
Once the NSLOOKUP shell is open, you will need to tell NSLOOKUP which DNS server you want to query. To do so, enter the SERVER command, followed by the DNS server’s IP address. You can also enter the server’s fully qualified domain name (assuming that it can be resolved) as an alternative to the server’s IP address.
Now that you have specified a DNS server for NSLOOKUP to use, you can query domains without receiving the non-existent domain error messages that you saw earlier (as long as you remain within the NSLOOKUP shell). To do so, you would simply type the domain name that you want to query. For example, if you look at Figure C, you can see where I have specified a particular DNS server and then queried an external and an internal domain.
Figure C: The error messages go away if you specify a DNS server
Now, let’s get back to the business of looking up a domain’s MX record. To do so, you need to issue a command that tells NSLOOKUP to query based on MX records. The command that you will have to use is:
SET QUERY=MX
Issuing this command by itself won’t give you any information about the domain’s MX record though. For that you have to actually query the domain by entering the domain name. If you look at Figure D, you will see that I have specified an MX query and then entered the production.com domain name. NSLOOKUP now returns a wealth of information pertaining to my domain’s MX record.
Figure D: When an MX query is specified, you can get a wealth of information about your domain’s MX record
As you can see, NSLOOKUP can provide you with a wealth of DNS server diagnostic information. However, NSLOOKUP is not limited to providing the types of information that I have discussed. The NSLOOKUP shell is actually a fairly rich interface with a rather large command set. You can view a list of the available commands and their syntax by entering a question mark at the NSLOOKUP prompt (note: you can not use NSLOOKUP /? to view the command set).
The NET command is used to manage requesters (networked computers), servers and network resources (network drives, printers, etcetera).
Most options of NET.EXE are also available in GUI style programs in Windows and OS/2, but for automating tasks nothing beats the command line interface of NET.EXE and its NT counterparts.
I "grew up" with OS/2 LAN Server's command line.
I automated many tasks using either batch files with NET.EXE or Rexx scripts with LAN Server RexxUtil.
After jumping on the NT train, it took me a while before I realized that I wasn't condemned to GUI style programs at all, as long as I had access to the Windows NT 4 and 2000 Server Resource Kit utilities.
Being an ex-OS/2 administrator, the first scripts I created for NT were (Regina) Rexx scripts, written for the Rexx version that comes with the Resource Kit.
After a while I switched to batch files combined with Resource Kit utilities.
To my surprise NT's batch language is almost as powerfull as a the Resource Kit's Rexx version.
One of the biggest problems when switching from LAN Server to NT is that many of NET.EXE's options have been moved to separate utilities in NT.
The following table and examples are meant as a cross reference: find the "original" LAN Manager/LAN Server command in the column on the left, and check the middle column to see what it translates to in NT.
Note that even when some NET commands remained the same, the options may still differ vastly.
Use NET HELP command to get online help.
In OS/2 you will get even more help on the available options using NET HELP command /O
Windows NT 4's help files contain, amongst others, a very helpful translation table too.
Look at the "Contents", "Windows NT Commands", "What's New or Different from LAN Manager?".
| Note: | | For NT I added several commands from the free PSTools toolkit. These tools can be used on local as well as remote systems. A must-have for Windows administrators. |
|---|
| LAN Server/LAN Manager and NT command translation | ||
|---|---|---|
| OS/2, LAN Server LAN Manager | Windows NT | Remarks |
| AT | AT | Schedule tasks |
| NET ACCESS | CACLS | Manage access. Alternative (non-native) commands for NT: XCACLS, SHOWACLS, RMTSHARE, SUBINACL, SECEDIT. |
| NET ACCOUNTS | NET ACCOUNTS | |
| NET ADMIN | RCMD (1) PSEXEC | IMHO NET ADMIN was NT's worst omission. On the other hand, RCMD (1) and PSEXEC may very well be the best replacements one could ever wish. |
| NET ADMIN /C \\server NET ACCESS local_path ... | XCACLS (1) unc_path ... PSEXEC \\server CACLS local_path ... | For files only, CACLS can be used on UNC based names as well. |
| NET ADMIN /C \\domaincontroller NET GROUP globalgroup ... | NET GROUP globalgroup ... /DOMAIN | |
| NET ADMIN /C \\server NET SHARE share ... | RMTSHARE (1) \\server\share ... PSEXEC \\server NET SHARE share ... | |
| NET ADMIN /C \\domaincontroller NET USER user_id ... | NET USER user_id ... /DOMAIN | |
| NET ADMIN /C \\server NET FILE ... | PSFILE \\server ... | |
| NET ALIAS | None (2) | |
| NET APP | None (2) | |
| NET APPPARM | None (2) | OS/2 Warp 4.5 (eComStation) only |
| NET AUDIT | None (2) | |
| NET COMM | None (2) | |
| None (2) | NET COMPUTER | |
| NET CONFIG | NET CONFIG | Display NetBIOS configuration information |
| NET CONTINUE | NET CONTINUE | Continue paused services |
| NET COPY | COPY XCOPY FCOPY (1) | |
| NET DASD | None (2) | |
| NET DEVICE | None (2) | |
| NET ERROR | DUMPEL (1) PSLOGLIST | |
| NET FILE | NET FILE | List files opened by remote computers |
| NET FORWARD | None (2) | |
| NET GROUP | NET GROUP NET LOCALGROUP | List or manage groups and group membership |
| NET HELP | NET HELP NET HELPMSG | Use NET HELP to display syntax. Use NET HELPMSG to display information on error messages. |
| NET LOG | None (2) | |
| NET MOVE | None (2) | |
| NET NAME | NET NAME | List or manage NetBIOS names |
| NET PASSWORD | NET USER user_id new_password [ /DOMAIN ] | The command RUNDLL32.EXE NETPLWIZ.DLL,UsersRunDll will start the GUI for changing passwords (by Administrators only).[ Thanks for Steve Pasikowski for pointing out an error in the previously published command ] |
| NET PAUSE | NET PAUSE | Pause services |
| NET PRINT | NET PRINT | |
| NET RIPLMACH | None (2) | OS/2 Warp 4.5 (eComStation) only |
| NET RIPLMCLAS | None (2) | OS/2 Warp 4.5 (eComStation) only |
| NET RUN | RCMD (1) PSEXEC | |
| NET SEND | NET SEND | Send messages to other users or computers |
| NET SESSION | NET SESSION | |
| NET SHARE | NET SHARE | In Windows Server 2003 the default permissions on shares have changed from Everyone Full Control to Everyone Read! Use the /GRANT:Everyone,Full switch to set permissions to the old default. |
| NET START | NET START | Start services |
| NET STATISTICS | NET STATISTICS | |
| NET STATUS | NET CONFIG and NET SHARE | |
| NET STOP | NET STOP | Stop services |
| NET TIME | NET TIME | Synchronize time with a remote computer, or display a remote computer's current time |
| NET USE | NET USE | NT's /USER switch makes this command extremely powerfull |
| NET USER | NET USER | List or manage users |
| NET VIEW | NET VIEW | List domains and workgroups (NT's /DOMAIN switch only only), computers, or shared devices |
| NET WHO | None (2) | IMHO this is NT's secondmost important omission. See NetWho and NetWho2 for an attempt to fill the gap. For small NT networks PSLOGGEDON may be a viable alternative. |
| Notes: | (1) | This utility comes with the Windows NT Server Resource Kit |
| (2) | There seems to be no command line equivalent available in NT. However, for most tasks GUI style utilities are available in NT. |
Lists information about the user.
finger [-b] [-f] [-h] [-i] [-l] [-m] [-p] [-q] [-s] [-w] [username]
| -b | Suppress printing the user's home directory and shell in a long format printout. |
| -f | Suppress printing the header that is normally printed in a non-long format printout. |
| -h | Suppress printing of the .project file in a long format printout. |
| -i | Force "idle" output format, which is similar to short format except that only the login name, terminal, login time, and idle time are printed. |
| -l | Force long output format. |
| -m | Match arguments only on user name (not first or last name). |
| -p | Suppress printing of the .plan file in a long format printout. |
| -q | Force quick output format, which is similar to short format except that only the login name, terminal, and login time are printed. |
| -s | Force short output format. |
| -w | Suppress printing the full name in a short format printout. |
finger -b -p ch - Would display the following information about the user ch.
Login name: admin In real life: Computer Hope
On since Feb 11 23:37:16 on pts/7 from domain.computerhope.com
28 seconds Idle Time
Unread mail since Mon Feb 12 00:22:52 2001
ac
passwd
who
whois
Displays, adds and removes arp information from network devices.
Short for Address Resolution Protocol, ARP is a protocol used with the IP protocol for mapping a 32-bit Internet Protocol address to a MAC address that is recognized in the local network specified in RFC 826. Once recognized, the server or networking device returns a response containing the required address.
ARP -d inet_addr [if_addr]
ARP -a [inet_addr] [-N if_addr]
| -a | Displays current ARP entries by interrogating the current protocol data. If inet_addr is specified, the IP and Physical addresses for only the specified computer are displayed. If more than one network interface uses ARP, entries for each ARP table are displayed. |
| -g | Same as -a |
| inet_addr | Specifies an Internet address. |
| -N if addr | Displays the ARP entries for the network interface specified by if_addr. |
| -d | Deletes the host specified by inet_addr. |
| -s | Adds the host and associates the Internet address inet_addr with the Physical address eth_addr. The Physical address is given as 6 hexadecimal bytes seperated by hyphens. The entry is permanent. |
| eth_addr | Specifies a physical address |
| if_addr | If present, this specifies the Internet address of the interface whose address translation table should be modified. If not present, the first applicable interface will be used. |
arp -a
Interface 220.0.0.80
| Internet Address | Physical Address | Type |
| 220.0.0.160 | 00-50-04-62-F7-23 | static |
The Physical Address or MAC address as shown above in the format aa-bb-cc-dd-ee-ff is the unique manufacturer identification number. This number should always be a unique address.
An example of how to change the above IP address 220.0.0.160 to 220.0.0.161 in this case would be:
arp -s 220.0.0.161 00-50-04-62-F7-23
If an IP address has already been assigned to the specific network adapter it is not possible to change that assigned IP address to a new address. In addition, networks italicizing DHCP, BOOTP or RARP will automatically assign the card an IP address, therefore, this command would not be utilized.
1. Also known as an admin, administrator, and gatekeeper this account is a super user on a computer and/or network and has complete control over it. When referring to a Unix / Linux computer this user is often known as root and on a Windows computer and network this user is often referred to as an administrator. However, each of these terms is interchangeable.
2. The highest level in a directory hierarchy. For example, in MS-DOS, the root of the primary hard disk drive would C:\.
Issue:Help with ping, winipcfg, and other network commands. Cause:It may Solution:Below is a Note: If you are not the root or admin of a computer, it is possible Arp Display or
The finger
The hostname
Ipconfig is a MS-DOS utility that Windows 2000 users
Pathping is a MS-DOS utility
The nbtstat MS-DOS utility that displays protocol
The net command
The netstat command is used to display the TCP/IP network
The nslookup MS-DOS utility that enables a user to do a reverse lookup on an IP address of a domain
The route MS-DOS
The tracert command in MS-DOS / Windows or the traceroute command in Unix / Linux and variants is
The whois command available in Unix / Linux variants helps
The winipcfg command available in Windows allows a user to
NOTE: Windows |
