Adding the IP Address in Redhat Enterprise Linux can be done by using the netconfig tool or by editing the network-scripts or by using the ifconfig command. While this procedure is tested on Redhat Enterprise Linux, I'm sure it should work on CentOS, Fedora and older Redhat versions.
Set IP Address using Netconfig
Netconfig is a utility in Redhat Enterprise Linux which allows you to add/modify the IP Address the system, the Netmask, default gateways and the Name Servers.
Launch Netconfig,
rhel5# /usr/bin/netconfig
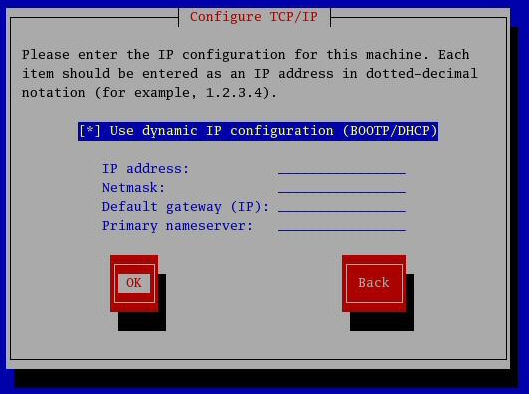
This launches a window as follows:
For static IP uncheck the "Use Dynamic IP configuration(BOOTP/DHCP)"
Now, enter the IP Address, netmask, Default Gateway & Primary Name Server.
Once done, restart the networking service
rhel5# service network restart
or to just reread the interface config files
rhel5# service network reload
This should set the IP Address.
Manually edit Interface configuration files
You can also manually edit the interface configuration files and add/modify the IP Address.
The Network interface configuration files are found in the directory
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
Let's say there are 2 interfaces eth0 & eth1. The files to edit will be
ifcfg-eth0 – For interface eth0
ifcfg-eth1 – For interface eth1
To add the IP Address for interface eth0, edit ifcfg-eth0
rhel5# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
rhel5# vi ifcfg-eth0
Enter the following Parameters
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=static
BROADCAST=192.168.1.255
HWADDR=00:0F:1F:2F:3F:4F
IPADDR=192.168.1.10
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
NETWORK=192.168.1.0
ONBOOT=yes
TYPE=Ethernet
Where
DEVICE indicates the interface
BOOTPROTO indicates if it is static IP or uses DHCP/BOOTP
The above sets the IP Address, Broadcast address, Network, Netmask etc.
Once done, save the file and restart the network service for the changes to take effect.
rhel5# service network restart
or to just reread the interface config files
rhel5# service network reload
Using ifconfig
This is dynamic and the change take effect instantly.
rhel5# ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.1.1 up
This sets the IP Address, Netmask and the default gateway on the interface